NEET PG 2025: Selecting the right medical college for your postgraduate (PG) studies after NEET PG is a critical decision that can shape your career. With hundreds of MD/MS/DNB programs across India, you should weigh factors like your specialty interest, course type, and college characteristics. Careful planning prevents costly mistakes.
The process can be broken down into two main steps: first, choose the PG degree and specialty, and second, evaluate the colleges offering that program.
Decide on Degree Type and Specialty
Choose your PG qualification and field of interest.
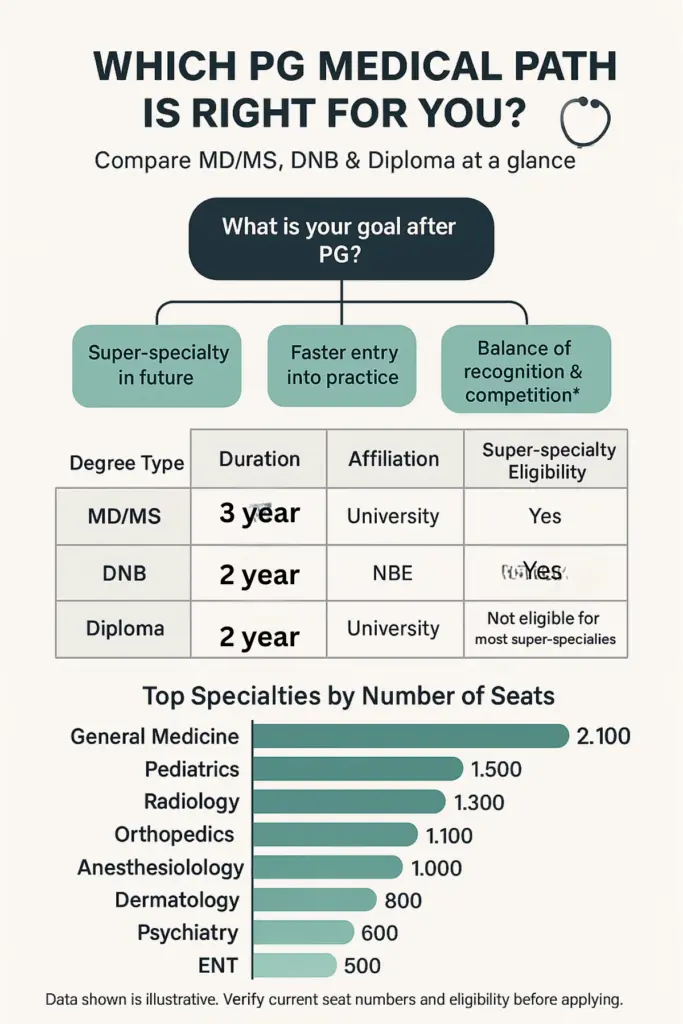
After NEET PG, decide whether you want a three-year MD/MS, a Diplomate of National Board (DNB), or a two-year diploma in medicine/surgery. MD/MS degrees are traditional university postgraduate programs, while DNB is awarded by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS).
Importantly, DNB is recognised as equivalent to an MD/MS. For example, the National Board of Examinations explicitly states that “the DNB course is approved by the Government of India and is considered equivalent to the postgraduate…programmes offered by medical colleges in India”
According to NMC regulations, MD/MS programs normally last 3 years (with a 2-year duration only if you already hold a recognised 2-year diploma in the same specialty), whereas diplomas are fixed at 2 years.
Plan accordingly, as MD/MS and DNB specialists can pursue super-specialty (DM/MCh) training, while diploma holders often have more limited options.
Next, prioritise your speciality interests. Ask yourself:
| NEET PG Counselling Guide 2025 | |
|---|---|
| MCC NEET PG Counselling Guide eBook 2025 | 📥 Download |
| DNB Counselling Book 2025 | 📥 Download |
- Which subjects do I enjoy? List specialties (e.g. Radiology, Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, OBGYN, etc.) by personal interest or career goals.
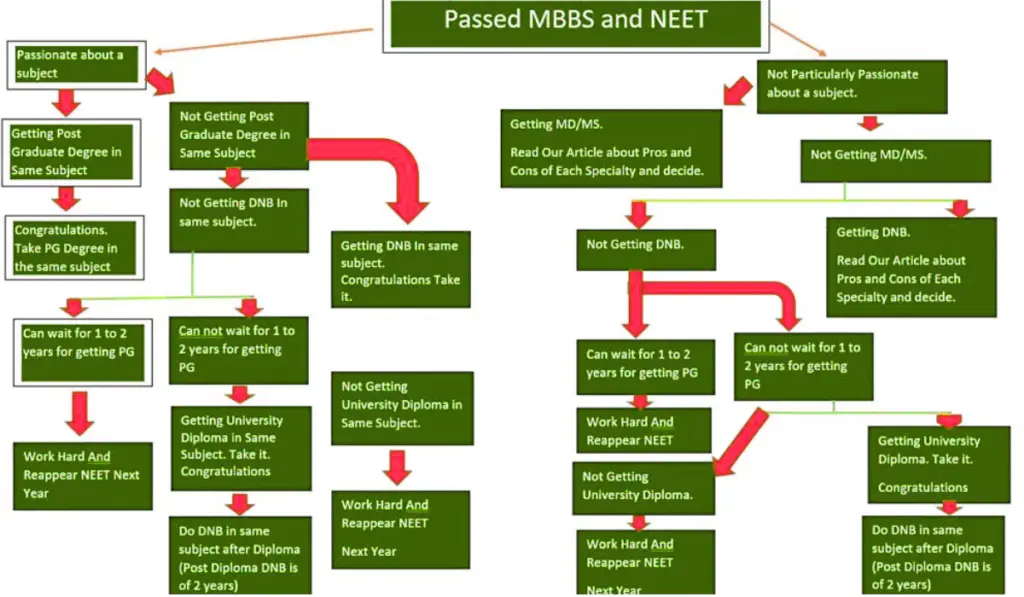
- What if I don’t get my first choice? Decide whether you would accept a diploma or a DNB in a related field if your top MD/MS program is unavailable, or if you’d prefer to re-attempt NEET next year.
- Do I want a degree or am I open to a diploma? While a diploma is shorter and sometimes easier to get, it is generally viewed as less competitive than a full MD/MS. For example, some surgeons prefer an MS over a shorter diploma in surgery for career reasons.
Having clarity on these questions ahead of NEET PG counselling will help you rank your choices. A structured fallback plan (e.g. first choice MD in X, second choice DNB in X, third choice MD in Y, etc.) is advisable.
NEET PG Branch Selection Flowchart
Evaluate Colleges and Programs
Once you know the degree and specialty you want, compare the colleges that offer that program. Key factors include:
Service Bond Requirements
- Many states require PG doctors to serve in rural or public hospitals for a specified period after graduation, or pay a penalty.
- Bond durations vary widely: some states like Delhi, Meghalaya, Manipur and Chandigarh have no mandatory PG bond, while others impose multiple years of service.
- For example, Rajasthan mandates a 5-year bond for government PG seats, and Assam even enforces a 10-year service bond for MD/MS graduates.
- These state bond rules are typically public information. Before choosing a college, check the exact bond terms (service location, duration, and penalty) at that college.
- A short or zero bond gives you greater freedom to move or work elsewhere; a long bond (or a high penalty) can restrict your early career moves.
Location (Distance and Environment)
- Proximity to home and the college’s setting affect quality of life.
- PG students rarely get frequent leave, so a college far from home can mean long, exhausting travel during breaks.
- Of course, you should not sacrifice educational quality solely for location, but between two similar colleges, one closer to home is often more convenient.
- Also consider the city’s climate, language, and living costs.
Faculty and Mentors
- The expertise and mentorship of faculty profoundly shape your training.
- Look for colleges with experienced and communicative teachers.
- Studies of medical education emphasise that knowledge of the subject, enthusiasm, and good communication are top qualities of an effective medical teacher.
- Working under highly qualified PG guides not only improves clinical skills but also offers better research training (thesis supervision) and networking.
- Many distinguished faculty work at reputed institutions, so college reputation can be a proxy for mentor quality.
Patient Load and Clinical Exposure
- One of the greatest advantages of government or large tertiary hospitals is high patient volume.
- As noted in a comparison of MD training, government institutions generally have a heavier patient load, while private institutions have fewer cases.
- If you’re in a surgical field or a specialty that benefits from diverse cases, a busier college means more hands-on experience.
- For example, a trauma surgery resident will get more cases in a large government hospital than in a smaller center.
- Make sure the college has a robust inpatient and outpatient census in your specialty.
- You can often gauge this by visiting the hospital website or asking current residents.
Reputation, Accreditation and Infrastructure
- Ensure the college and program are recognised by the National Medical Commission (NMC) and have the required departments and facilities for your specialty.
- Also consider the institution’s overall reputation and ranking.
- For instance, top-ranked MD colleges in India include AIIMS Delhi, CMC Vellore, KMC Manipal, PGIMER Chandigarh and KGMU Lucknow, reflecting excellent infrastructure and faculty.
- While you may not access these elite centers, reviewing how a college ranks in National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) or other surveys can inform you about its academic environment.
- Facilities like well-equipped labs, intensive care units, and libraries also matter for your training.
Summarizing key considerations:
- Service Bond: Compare state and college bond rules. A 1–2 year bond is typical; anything 3+ years is stringent.
- Location: Proximity to home and teaching hospital environment.
- Faculty: Qualified, caring mentors (studies show subject-matter expertise and communication are crucial qualities).
- Clinical Exposure: High patient load boosts learning.
- Reputation & Resources: Accreditation, college ranking, lab and library facilities.
Overall, choose the program and college that best align with your long-term goals. By considering the degree type, your specialty preference, and the college’s bond, faculty and case load (with data-backed insights), you can make an informed choice.
This thorough evaluation ensures that your postgraduate training is in an environment where you can learn the most and build your career successfully.

